

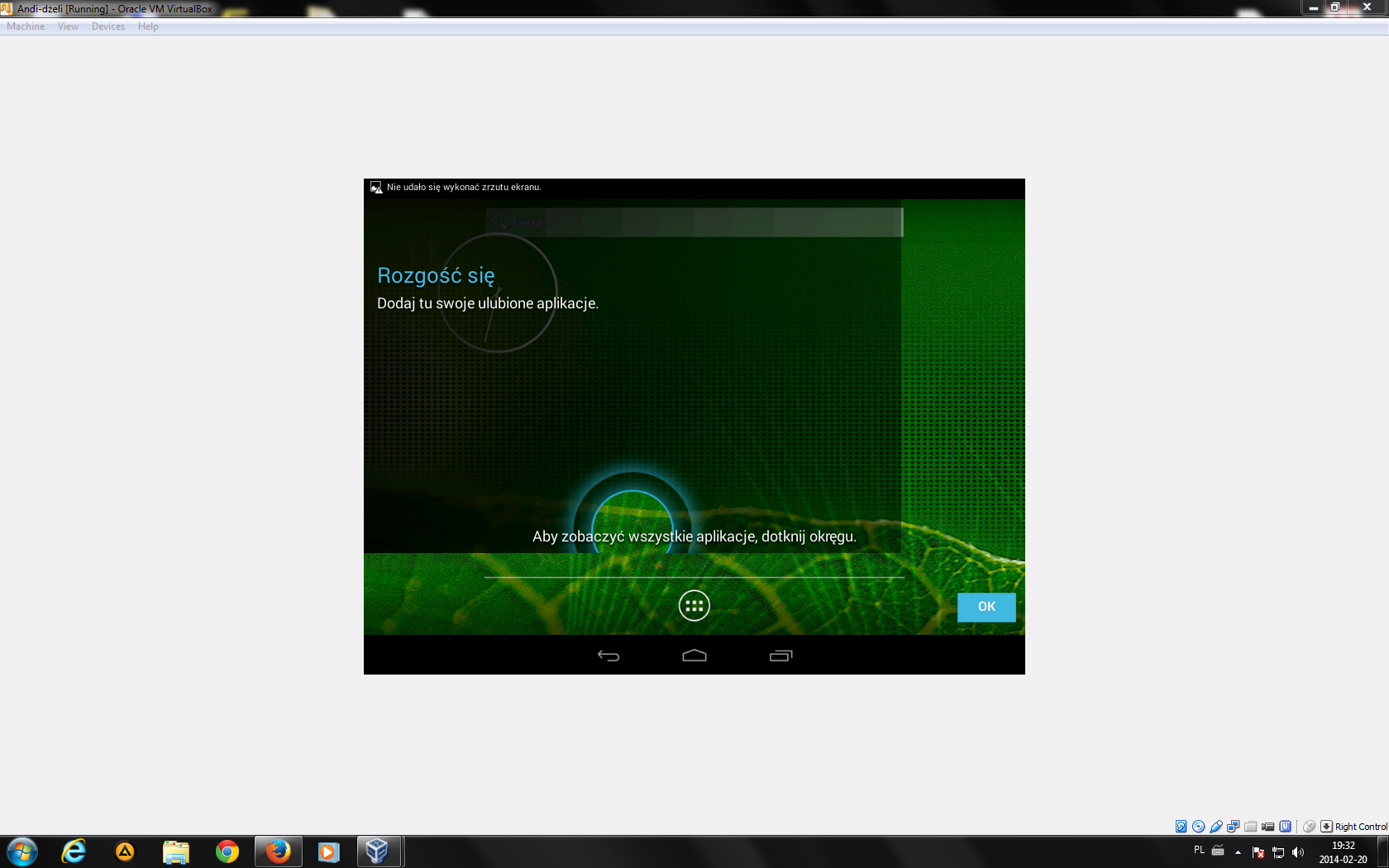
When it is completed, select “Run Android-x86”.Īndroid 4.0 will now boot up.
The installer will then proceed to do its job. If you are a developer or intend to use this full time, select Yes.
When it prompts you whether you want to enable read-write for the /system directory, choose No if you just want to test and try out Android 4.0. Select “ext3” as the filesystem to format to. For this tutorial, I will go through the installation mode.
Virtualbox android install#
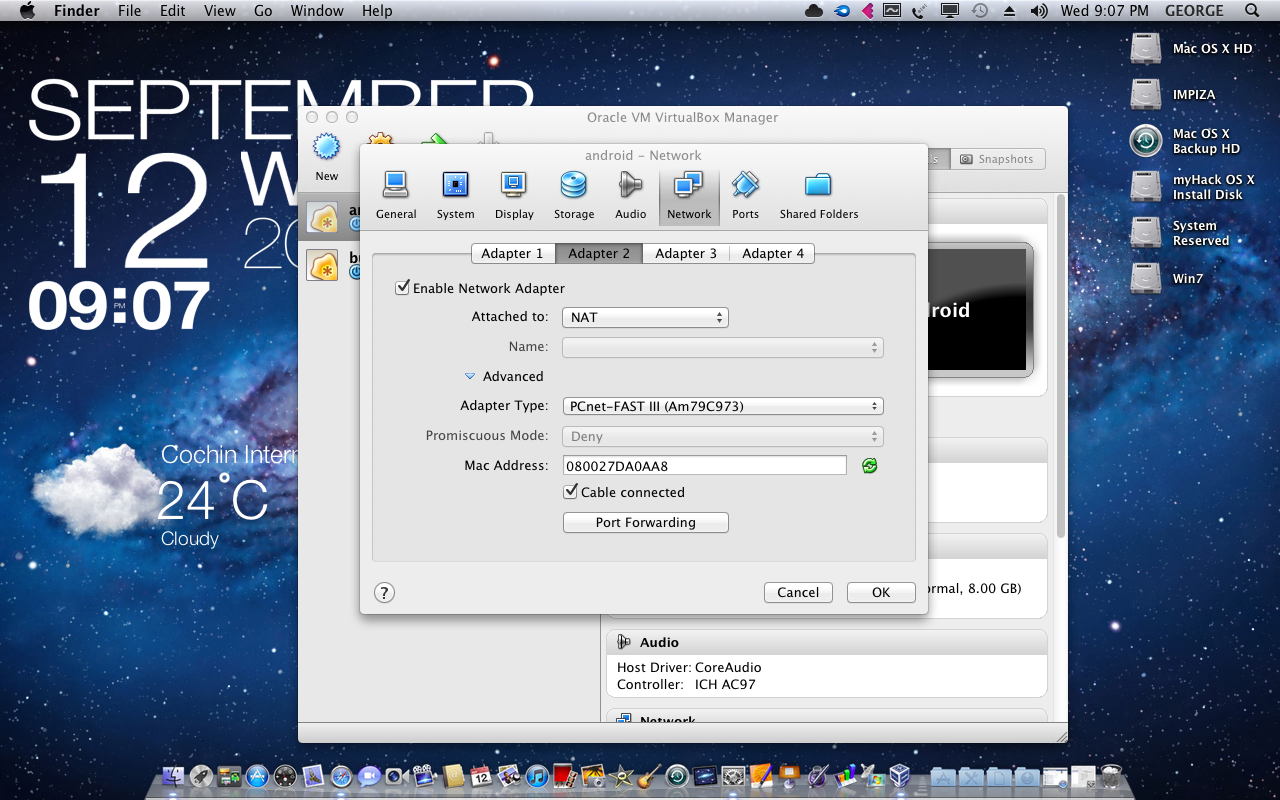
You have the choice to run Android without any installation (live-CD mode) or install it in your VM. This is what you will see on first boot up. Once you are back in the main screen, click “Start” to run the installation. You should see something like this:Ĭlick OK to save the changes. Under the Attribute section, click the CD icon and select the Android 4.0 iso that you have previously downloaded. Next, go to Storage and select the Cd-rom entry. On the left pane, select “System” and make sure that CD/DVD-ROM is checked and is the first in the boot order. Once you have done creating the VM and is back to the main screen, highlight the new VM and click the Settings button. It is a good idea to set it to “Dynamically Allocated” and set the size to 8.0GB. Select “Create New Hard Disk”, followed by “VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)” as the file type.ĥ. Set the base memory to 1000MB (though I think that 512MB will work as well).Ĥ. Give your new VM a name (such as Androidx86) and set the Operating System to “Linux” and the version to “Linux 2.6”.ģ. Assuming that Virtualbox is already installed in your PC, open your Virtualbox and create a new virtual machine. The filesize is about 180mb, so it will take about 10 – 15 mins if you have a broadband connection.Ģ. The one that I am using for this tutorial is “ android-x86-4.0-RC1-asus_laptop.iso“. There are several versions that you can download. Download Android 4.0 RC here (scroll down the list till you see the “Android-x86-4.0-RC1” section). A host machine with at least 1GB of RAM to spare.ģ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
